Chattanooga, which was named a Heartland Forward 2025 Secret Sauce City for the second time, just made history. With the announcement of the EPB Quantum Center℠, this Tennessee city became the first in America to launch a commercial quantum network, a significantly more advanced and powerful computing network than those traditionally used. It’s a gold medal moment, the kind that puts a city on the map for what it will become: a leader in the next era of technology—the quantum revolution.
What is quantum computing?
Quantum computing is built upon quantum physics, the study of how the universe acts at its smallest scale—on the atomic and molecular level.
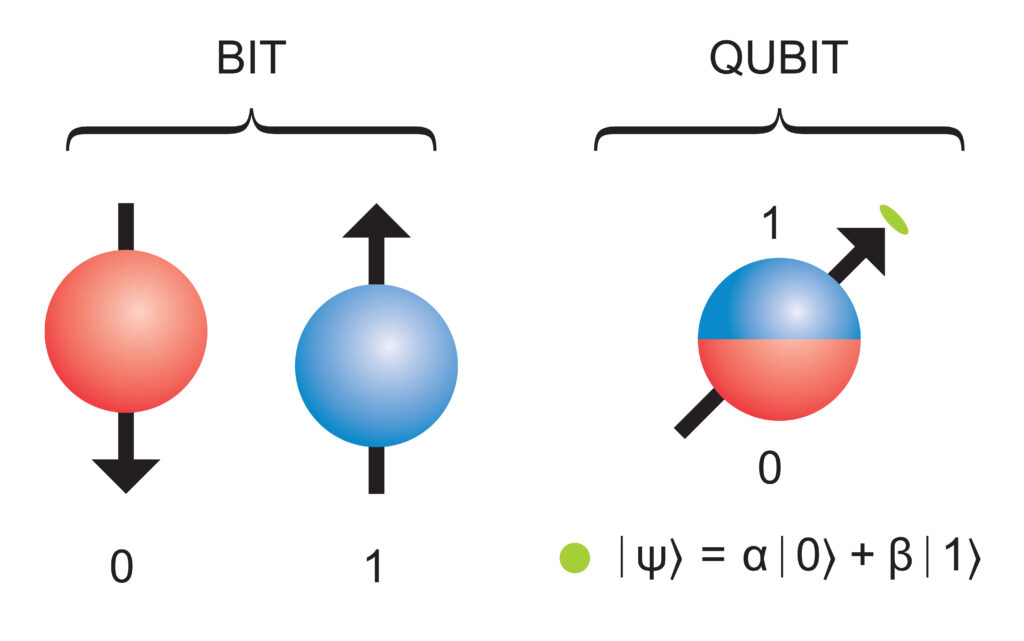
Quantum computing is more advanced than classical computing. Classical computers, like phones and laptops, encode data in a binary pattern using 0s and 1s. Everything digital, from a text message to a Spotify song, is a long string of binary digits, or bits. For example, when the letter “A” is typed on a keyboard, the input received by the computer is “01000001” and thus it knows to put “A” on the screen.
Quantum computers, on the other hand, encode data as quantum bits, or qubits, which are different from regular bits because the qubit is able to represent different states of energy; 0, 1, or both—at the same time. Being in two states of energy at the same time can be difficult to comprehend, because large objects like humans, cannot maintain more than one state of energy at a time. However, small objects, like atoms and molecules can. Spinning a coin can provide useful imagery to understand this concept. While a coin spins, it can be interpreted as both heads and tails—which is similar to what a qubit is doing, existing in multiple states of energy. Smaller objects studied in quantum physics can even be manipulated by science to represent 0, 1, or both. The ability to have multiple states of energy in the same atom is what makes quantum computing so revolutionary.
Why does quantum computing matter?
Qubits allow quantum computers to process data exponentially faster than traditional computers that use bits. Two bits contain two pieces of data, but two qubits can contain four pieces of data, as one qubit contains multiple energy states, representing 0 and 1. A string of ten qubits can store over 1,000 pieces of data. This exponential increase is revolutionary when applied in areas such as:
- Health and wellness with drug discovery and chemical research
- Regional competitiveness with financial modeling that can drastically reduce business risk
- Innovation and entrepreneurship by providing better models and cost efficient manufacturing
Quantum computing is positioned to take artificial intelligence to a whole new level. AI requires lots of computational power and quantum machines can provide exponentially more than traditional computers. With the power potential of quantum computers, AI models can be trained faster and more efficiently to solve the unimaginable problems of the future.
Quantum technology is the force behind Chattanooga’s bold new $22 million venture. The EPB Quantum Center℠, to be finished in 2026, was developed in partnership with IonQ, a leading commercial quantum computing company and the Chattanooga Electric Power Board (EPB), a utility company that supplies 100% city-wide high-speed internet access to “Gig City®”, Chattanooga’s nickname. The facility will allow public and private users to get connected to a quantum network and use quantum computing infrastructure, speeding up medical discoveries, research uncoverings, and business developments.
Originally an industrial town centered around natural resources used in iron and steel production, Chattanooga is laying the tracks for the future of computing by building a quantum economy and coexisting quantum ecosystem that includes everyone: entrepreneurs, researchers, students and citizens alike. The Chattanooga Quantum Collaborative (CQC) is leading the charge on creating public-private partnerships to fill the EPB Quantum Center℠ with quantum users. Acting as a convener of Tennessee’s quantum assets, CQC is building the quantum ecosystem with workforce development programs and innovative partnerships with startups and private companies.
- The University of Tennessee at Chattanooga (UTC), a founding member of the CQC, is training a quantum ready workforce at the UTC Quantum Center. Quantum Information Science and Engineering (QISE) courses and certifications are offered to undergraduates and graduates, as well as a non-credit course for introduction.
- The Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy, is testing quantum equipment on EPB’s commercial network. ORNL is demonstrating how government discoveries can rely on private sector innovation.
- CQC offers a learning center, where children as young as kindergarteners are learning the basics of quantum science, as it aligns with the Tennessee K-8 Science Standards, alongside lessons for high schoolers and adult learners.
These efforts and the creation of the quantum ecosystem is what differentiates Chattanooga’s approach and makes it so powerful. The development of a supportive workforce in coordination with existing industry and government means Chattanooga’s quantum ecosystem will be sustainable. Aligning research institutions with public utilities and private innovators means Chattanooga’s quantum sector will grow in sync, not in silos.
The implications of Chattanooga’s quantum ecosystem stretch beyond city limits, proving tech leadership belongs in the heartland. With infrastructure, vision and partners rooted in the heartland, any state can lead in the industries of tomorrow, like AI and quantum computing. Chattanooga is offering a blueprint for regional competitiveness, American innovation and a fast, smart and technology-inclusive future.

